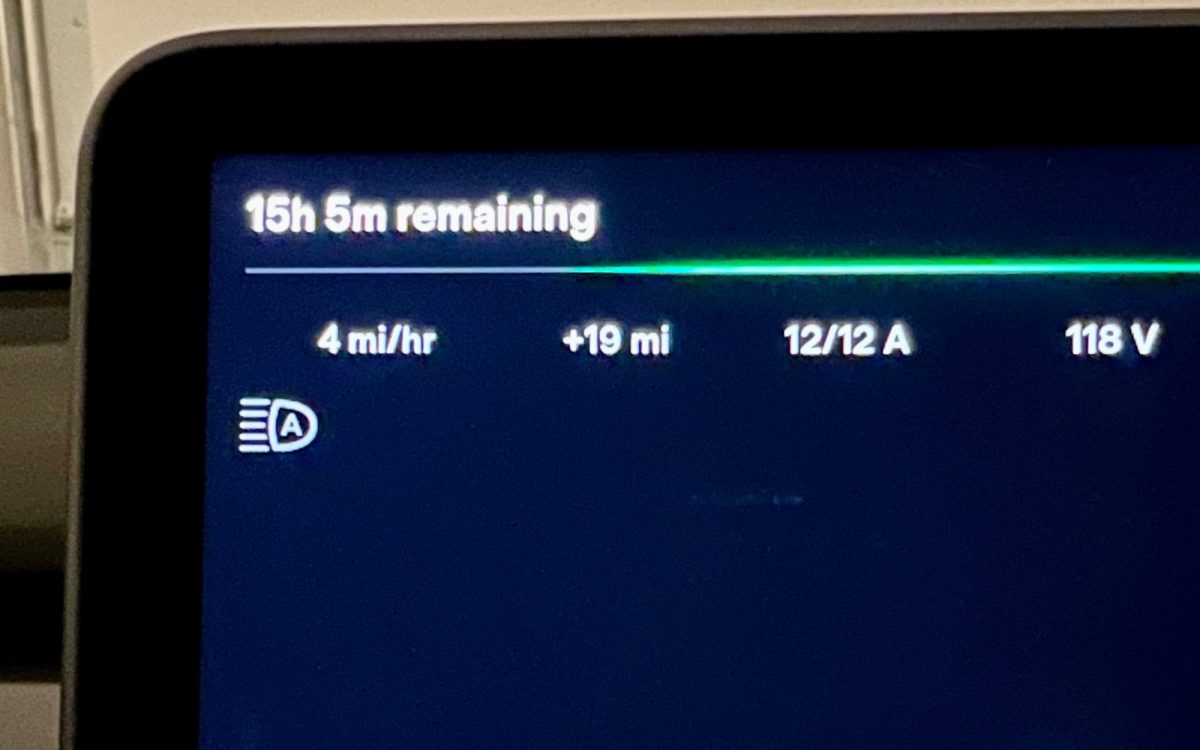
Consumers transitioning from gasoline combustion cars to electric vehicles may find it odd to see charging speeds displayed in miles per hour. The car is obviously stationary while charging, so why display the charging speed this way? Well, it is actually the number of miles added back into the battery per hour of charging, to be more exact.
Energy storage for EVs is measured in kilowatt-hours, So a 75 kWh capacity battery can output 25 kiloWatts of power for 3 hours of driving, for example. While most people have some idea how much is a gallon of gasoline, it is less commonly understood how much 1 kWh of energy really is. For this reason, Tesla and other early EV automakers began to display charging speeds in mi/h as well as kilowatts (kW) to give drivers context for how quickly energy is flowing into the battery.
The mi/h number is derived from the charging speed in kilowatts (kW) and the driving energy efficiency of the car. For example, if an EV that needs 300 watt hours of energy to travel one mile (Wh/mi) is charging at 150,000 Watts (or 150 kW) at a fast charging station, the display will read a charging speed of 500 mi/h.
Realistically it does not translate to 250 miles of range added in half an hour, because the charging speeds are fastest when the battery is nearly empty, and speeds slow down significantly after the battery is more than half full.
How many mi/h can I expect while charging?
Level 1 charging (120v x 12 amps) will typically yield 3-5 miles of range added per hour (as pictured in the photo above), depending on vehicle size and weight. Stepping up to 240-volt Level 2 charging, you can typically add between 20 and 45 mph of range back into the battery. Level 3 DC charging is an order of magnitude faster using 400-volt systems, EVs can charge at speeds of 600-700 mph+ under optimal conditions before the speeds begin to taper off.
Related: How To Make A Tesla Charge Faster At Home
Considering buying a Tesla? Use our referral link to get $2,000 off, and help support our content.